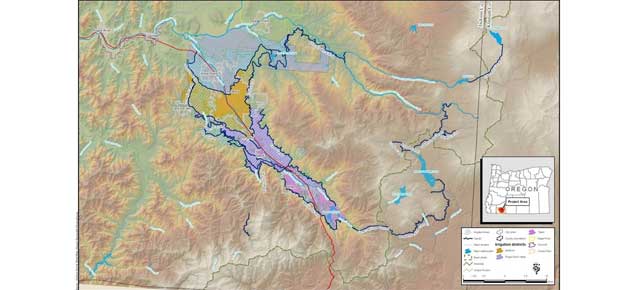
The WISE (Water for Irrigation, Streams and the Economy) project was a multi-faceted partnership between water users and stakeholders working proactively to improve water quality and quantity in the Little Butte Creek and Bear Creek watersheds for irrigation, aquatic habitat, and other uses in an economically and environmentally feasible manner. The WISE project was located within Jackson County. The project area included Bear Creek, Little Butte Creek, and tributaries and reservoirs that serve the Bear Creek and Little Butte Creek watersheds. The WISE portion of the Bear Creek Watershed included six municipalities within its boundaries, including the Cities of Medford, Ashland, Talent, Central Point, Phoenix, and Jacksonville.
Agriculture was identified as a significant land use in the two basins and the agricultural lands are primarily served by the Talent, Medford, and Rogue River Valley Irrigation Districts. In the Rogue River Valley, 35,000 acres of farms are supported by irrigation water delivered by these three districts. The current irrigation system was an arrangement of mostly open canals that flow through six reservoirs: Four Mile Lake, Fish Lake, Howard Prairie Reservoir, Hyatt Reservoir, Agate Reservoir and Emigrant Lake, and intersect with Bear Creek and Little Butte Creek and their tributaries at various points.
Governor’s Designation Letter (PDF)
Declaration of Cooperation (PDF)
Problem Statement
The irrigation infrastructure was outdated and was cause for a significant amount of water loss throughout the system. The WISE project was needed because the Little Butte Creek and Bear Creek watersheds suffer from unreliable irrigation water supplies and degraded water quantity and quality for native anadromous salmonids and for other uses during low flow periods. Specific goals of the WISE project were to:
- Improve efficiency of water deliveries to the Medford, Rogue River Valley, and Talent irrigation districts
- Improve irrigation water supply reliability for the Medford, Rogue River Valley, and Talent irrigation districts
- Improve water conservation systemwide
- Improve water quantity, water quality, and water reliability for native anadromous salmonids
- Improve aesthetics and recreation values of reservoirs, streams, and rivers
- Improve water quality at the Robert Duff Water Treatment Facility intake by improving water quality in Little Butte Creek
- Incorporate the most cost-effective solution for the reliable reuse of effluent from the Regional Water Reclamation Facility’s future discharge permit requirements into the WISE Project
Results
In December 2009 a preliminary feasibility report was completed. The purpose of the preliminary feasibility study was to complete a technical screening of conceptual projects that could address the Oregon Solutions WISE project, Declaration of Cooperation. From the feasibility study two top options emerged. Potential projects screened through this phase will be further developed and evaluated in a subsequent feasibility study/environmental impact statement. Additional engineering studies will be completed as project alternatives are further developed based on the recommendations of this preliminary feasibility report.
In 2012 WISE successfully competed for an Oregon Water Resources Department (OWRD) grant of $243,000 to conduct a cost benefit analysis. The analysis specifically quantified project components, including piping, pressure levels, hydro power, reclaimed effluent, increasing reservoir storage and other topics. Oregon Solutions 2012
At the WISE partners’ request, Governor Kitzhaber designated WISE an Oregon Solutions project. He appointed Senator Jason Atkinson and Representative Peter Buckley as co-conveners. The project team had more than forty members. The kickoff meeting was in January 2012 and its final meeting was August 2012. Oregon Solutions helped the team achieve three main goals: identify environmental impact statement funding, create a multi-year plan and recommend a governance structure to implement the plan.